Breast inflammation most affects nursing women.How to treat these complications?<
12.10.2021/ Barbora Košňarová/ Articles/ 0 Comments
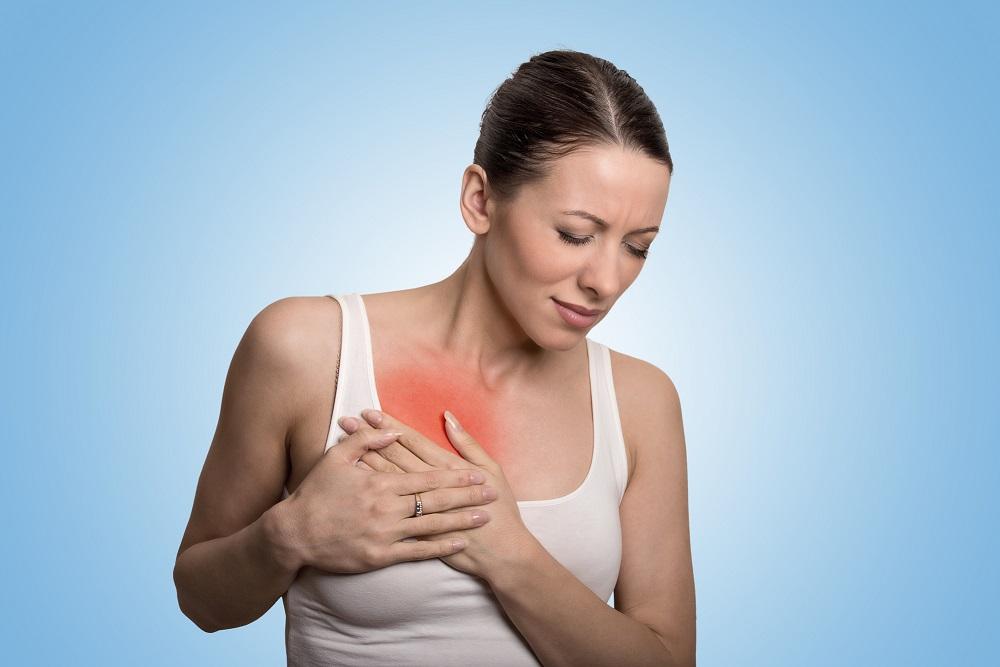
Do you suffer from unpleasant breast pain, which is sensitive to the touch, strongly red and significantly swollen?The blame will most likely be mastitis or inflammation of the mammary gland.This disease is mainly faced with nursing women, but may also appear outside lactation.Treatment of problems depends on their primary cause and usually involves administration of antibiotics.
What is breast inflammation?
A very painful inflammatory disease that affects nursing women (usually 3 usually 3 (usually 3.week after delivery).However, it does not avoid patients who are not one of fresh mothers or the male population part.Depending on who is struggling with this problem, the following problems are set aside:
Mastitis should be distinguished from similar problems such as clogged milk pipeline (milk retention) as these health problems require a different treatment than breast inflammation.How to know which of the problems is?When the milk pipeline is blocked, which is significantly more common in the puerperium.It is painful to the touch and its surroundings tend to be slightly red.
In the case of mastitis, a painful lump is also formed in the affected area, but unlike clogged lacts, the redness of the area is very intense and often other symptoms including fever.In addition, there may be a number of reactive changes in the mammary gland, such as fat necrosis (resulting in trauma) or bleeding necrosis (caused by anticoagulant treatment).
The causes of mastitis
Bacteria from a group of streptococci and staphylococci that live on human skin are usually an inducing factor.Especially various small cracks or wounds on the nipple can be the entrance gate of the infection.But this is not the rule.The breast inflammation also occurs in people who do not experience any nipple injury.
For example, the cause of nursing women may be the cause of milk in the milk pipeline and easier penetration of bacterial infection into the body when the child is attached to the breast.Higher risk that breast inflammation occurs is at risk of weakened immunity, for example due to diabetes, AIDS or other less or more serious diseases.
Of course, mastitis can also affect non -breastfeeding women.In this case, it is necessary to seek physicians as quickly as possible and focus on what the development of unpleasant symptoms has caused.The causes of the problems tend to be different and in some cases can cause breast inflammation abscess.In diagnosis it is important to distinguish dangerous inflammatory breast cancer.
What is breast inflammation symptoms?
Whether you suspect breast inflammation during breastfeeding, or problems have occurred during menopause, you will surely think about what difficulties it is possible to know that it is indeed an inflammation of the mammary gland.Initial symptoms include tension in the affected area and increased sensitivity to touch.Breasts tend to be significantly red and hot to the touch, they can swell and inflammation is also accompanied by unpleasant pain.
To make matters worse, an inflammatory fluid or even pus and a small amount of blood often flows out of the affected breast.Inside can also create a small painful lump.In addition, there are overall symptoms such as fever, chills, joint and muscle pain, increased fatigue, overall weakness, but also nausea or vomiting.
If the breast inflammation develops in a fresh mother, breastfeeding is very difficult and painful for her.It is also quite common to move inflammation from one breast to another, which usually means that bacteria spread through blood and cannot be solved without antibiotics.In some cases, the shape of the nipple may even change due to inflammation.
Types of mastitis
Doctors in practice distinguish two main types of breast inflammation.These are mainly inflammations caused in Puerperius (puerperium) and inflammations that appear outside it, which can have a variety of different causes.The individual symptoms and of course the necessary treatment may also differ partly.
Puerperal mastitis
This type of mastitis develops in patients in connection with pregnancy, breastfeeding and weaning of the baby from breast milk.Most often, puerperal inflammation of the mammary gland affects nursing women in 2.up to 3.week after delivery.The firstborn marks become ill about twice as often as patients who already have a offspring.About a quarter of cases then inflammation affects both breasts.
Regarding the disease cause, the development of complications is most commonly responsible for a gram -positive bacterium called Staphylococcus aureus.Furthermore, they may be other staphylococci or various streptococci.Depending on the entry of the breast, mastitis are divided into interstitial (bacteria penetrate the defitter cover, such as ragades or fisura) and parenchymatous (infections are spreading back through the outlet of the lactic to the parenchyma gland).
Puerperal breast inflammation is often the result of long -term problems associated with breastfeeding, which also worsens the psychological condition of the fresh mother.Risk factors are mainly poor breastfeeding technique, which increases the likelihood of milk retention, too tight or nylon linen, postpartum anemia, increased fatigue, excessive motion after delivery, menopause, injuries, poor hygiene or even a mother's failure.
Symptoms of Puerperal Mastitis
What breast inflammation can have symptoms in breastfeeding?If breast inflammation caused breastfeeding or weaning of the baby from breast milk, the first symptom the patient records is usually severe pain of the affected breast.The skin here is swollen, reddish and sensitive.In addition, women often complain about the feeling of tension and heat in the affected area, the skin is much warmer than its surroundings.
Out of total symptoms are mainly temperature higher than 38 ° C, shake, increased fatigue, joint and muscle pain, overall seizure, nausea and headache.In the armpit, women may feel reactively altered nodes that tend to be painful, and ragades appear on the pectoral court.Breastfeeding is usually very unpleasant, which some women lead to its rejection.
Milk of the affected breast contains a higher proportion of sodium and chlorine so it has a salty flavor.This usually does not matter to infants as they can adapt to this change quite easily.Therefore, children do not need to wean milk and regular breastfeeding can even help with the removal of an obstacle.However, it is necessary to stop the lactation in stubborn and recurring inflammations.
Puerperal mastitis
The second type of breast inflammation is non-puerperal mastitis, a heterogenic group of diseases that may have a number of different causes.This kind of difficulty most often occurs in the age of 20 to 40.Typical symptoms include redness, swelling of the affected area, significant pain, but also swollen lymph nodes, palpable lump or change of nipples.
Granulomatous and plasmocytic mastitis
Granulomatous (lobular) breast inflammation occurs mainly in women under 40 years of age, even with a longer time away from birth.The inflammatory bearing is relatively stiff and its part is formed by granulation tissue.The etiology of this problem is unknown, but one of the theories assumes that the intermittent hyperprolactinemia that causes medicines, hormones or stress is to blame.
Plasmocytic mastitis also represents chronic breast inflammation.In this case, however.In addition to typical symptoms, the disease also causes dense secretion from the nipple, and after acute symptoms resources in the breast of solid resistance.Treatment in both cases lies in excision (operative withdrawal).
Ductectasia and Subareolar Absces
In the case of ductectasia, large outlets (Dukt) are expanded, where secretions gradually accumulate.This problem occurs in women around the age of 30 to 60 years and smoking is a significant risk factor here.Subareolar abscess is then due to the obliteration of the milk pipeline with papilloma (benign tumor of the epithelium) or tile metaplastic epithelium.Due to these complications, it is swelling up to abscess, the pain in the nipple area is typical and purulent discharge occurs.
Peripheral breast abscess
This problem is not too common.It usually affects women suffering from diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis or granulomatous mastitis, but may also occur with steroid treatment, trauma and other predisposing conditions.The treatment of such an abscess is standard and consists of incision and drainage or repeated aspiration, which is also accompanied by treatment with antibiotics.
Fistula
Another cause of non-artral mastitis may be a ductal fistula that arises, for example, after the incision and drainage of abscess or after biopsy.Previously, fistulas were also formed in the spontaneous emptying area.Treatment is based on operative removal of fistula and administration of antibiotics.
Inflammation associated with skin infection
Primary skin infections (abscess or cellulite) may also occur in patients, which mainly affects the lower quadrants of the breast.Such inflammations are repeatedly threatened mainly for obese women, patients with large breasts or those who do not care enough for personal hygiene.Staphylococcus aureus is usually behind the development of difficulties, but mycotic infections may also be to blame.Another problem is the sebaceous cysts that are infected or other skin problems.
Less frequently infections
In addition to the above -mentioned factors, breast inflammation may also cause other types of infections.Doctors distinguish, for example, tuberculous mastitis that is relatively rare in our conditions.Typical symptoms of these health problems include fistulas that flow to the breast surface or abscess.
In a sclerotic form, the glandular body can harden, which significantly makes it difficult to distinguish this disease from breast cancer.Therapy then lies mainly in surgery and administration of antituberculotics.Even more rarely, the breast can affect some of the following diseases:
Infection after surgery
Breast inflammation may also occur in patients who have undergone breast biopsy, mamotom biopsy, open biopsy after stereotactic location or sentinel node biopsy.The infection becomes apparent about the second to the third day after the procedure.A characteristic feature of the difficulties is intense redness of the skin around climbs and breast pain.At the same time there is a smaller hematoma or serom in the wound.
Infectious complications after oncochirurgical procedures that the patients underwent due to diagnosed breast cancer is solved mainly during hospitalization.In the late postoperative period they are rather rare, which also applies to inflammation of the mammary gland, armpits and upper limbs on the affected side in women who have undergone complex treatment of breast cancer.
Diagnostics
If you suspect your mammary gland inflammation, it is advisable to consult another solution with a gynecologist or other doctor.Depending on whether she is a nursing woman, not a woman, a man or a newborn, it is necessary to carry out the necessary examinations.For example, a doctor may indicate breast examination with ultrasound to detect abscesses, mammography or breast sample sample sample.
Treatment of breast gland inflammation
When it comes to breast inflammation during breastfeeding, it is important to first distinguish this health problem from the retention of milk that can gradually develop in mastitis.Infant usually does not need to be shut down from milk.Regular breastfeeding with sufficient milk drain can cause unpleasant difficulties to retreat.
If the patient does not have high fever, it is often enough to learn a woman about the right breastfeeding technique, dispel her concern and support the efforts to feed the newborn.It is first recommended to breastfeed from a healthy breast before switching to the affected person.After the end of breastfeeding, the woman should spray (despite pain), while the milk will be yellow and dense.However, the patient should be relieved.
A gentle massage will also help better milk outflow.However, if it is a persistent inflammation or recurrent complications, most likely it will be necessary to stop lactation.As with another disease, the woman should follow the resting regime, rest sufficiently and regularly replenish liquids.
In addition, patients usually use antibiotics for breast inflammation.In the case of puerperal mastitis, mainly anti -zaphylococcal antibiotics, ie oxacillin, cephalosporins 1.and 2.generation or aminopenicillins with inhibitors.In case of hypersensitivity it is then possible to deploy macrolide antibiotics or clindamycin.Early treatment will help prevent abscess and significantly reduce the repeated incidence of mastitis.
Most antibiotics penetrate the breast milk, which may have a significant effect on the intestinal microflora of the infant.At the same time, a number of difficulties may develop.Therefore, the application of antibiotics, their specific type and dosage during lactation must be well considered.Patients can then apply moist or dry heat or cottage cheese wrap and the affected area can also be iced.
As regards the second type of inflammation, the treatment of non-puerperal mastitis always depends on the cause that is due.Patients are deployed antibiotics, various surgery (operative removal, cutting, drainage) and doctors also serve various non -steroidal anti -inflammatory drugs and other medicines.
Sources: Levret.cz, wikiskripta.EU, Stefajir.cz


 Tags:
Tags: Prev
Prev







